1876 Republican National Convention
| 1876 presidential election | |
  Nominees Hayes and Wheeler | |
| Convention | |
|---|---|
| Date(s) | June 14–16, 1876 |
| City | Cincinnati, Ohio |
| Venue | Exposition Hall |
| Candidates | |
| Presidential nominee | Rutherford B. Hayes of Ohio |
| Vice presidential nominee | William A. Wheeler of New York |
| Other candidates | James G. Blaine Benjamin H. Bristow |
The 1876 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held at the Exposition Hall in Cincinnati, Ohio on June 14–16, 1876. President Ulysses S. Grant had considered seeking a third term, but with various scandals, a poor economy and heavy Democratic gains in the House of Representatives that led many Republicans to repudiate him, he declined to run.[1][2] The convention resulted in the nomination of Governor Rutherford B. Hayes of Ohio for president and Representative William A. Wheeler of New York for vice president.
The Republican ticket of Hayes and Wheeler went on to lose the popular vote to Democrats Samuel J. Tilden and Thomas A. Hendricks in the election of 1876, but won the electoral vote after a controversy which was resolved by the Compromise of 1877.
Overview[edit]
The convention was called to order by Republican National Committee chairman Edwin D. Morgan. Theodore M. Pomeroy served as the convention's temporary chairman and Edward McPherson served as permanent president.
The principal candidates at the convention included Senator James G. Blaine of Maine, the former Speaker of the House; Senator Oliver P. Morton of Indiana; Secretary of the Treasury Benjamin H. Bristow of Kentucky; Senator Roscoe Conkling of New York; Governor Rutherford B. Hayes of Ohio; and Governor John F. Hartranft of Pennsylvania. James Russell Lowell, well-known poet and a professor at Harvard College, spoke on behalf of Hayes.[3]
Two candidates, Benjamin Bristow and Marshall Jewell of Connecticut, were serving as Cabinet members in the Grant administration.
Presidential nomination[edit]
Presidential candidates[edit]
.jpg/350px-1876_Republican_National_Convention_-_Ohio_(cropped).jpg)
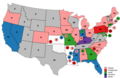
Blaine led after the first ballot, but had only 285 of the 378 delegates required to secure the nomination. Morton, Bristow, and Conkling each had around 100 delegates, while Hayes and Hartranft each had around 60. The second, third, and fourth ballots saw similar results, but Hayes began to surge on the fifth ballot, passing Morton and Conkling to secure third place after Blaine and Bristow. The sixth ballot saw Blaine rise to 308, but, with the other candidates fading, Hayes continued his surge, moving into second place. After the sixth ballot, the Bristow, Conkling, Morton, and Hartranft supporters withdrew their candidates' names from consideration, leaving Hayes as the sole focus of opposition to Blaine. With the other candidates gone, Hayes won a narrow majority on the seventh ballot and secured the nomination.
| Presidential Ballot | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ballot | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th |
| Hayes | 61 | 64 | 67 | 68 | 104 | 113 | 384 |
| Blaine | 285 | 296 | 293 | 292 | 286 | 308 | 351 |
| Bristow | 113 | 114 | 121 | 126 | 114 | 111 | 21 |
| Morton | 124 | 120 | 113 | 108 | 95 | 85 | 0 |
| Conkling | 99 | 93 | 90 | 84 | 82 | 81 | 0 |
| Hartranft | 58 | 63 | 68 | 71 | 69 | 50 | 0 |
| Jewell | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Washburne | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
| Wheeler | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Not Voting | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
Presidential Balloting / 3rd Day of Convention (June 16, 1876)
-
1st
Presidential Ballot -
2nd
Presidential Ballot -
3rd
Presidential Ballot -
4th
Presidential Ballot -
5th
Presidential Ballot -
6th
Presidential Ballot -
7th
Presidential Ballot
Vice Presidential nomination[edit]
Vice Presidential candidates[edit]
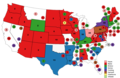
Five names were presented to the convention for the vice presidential nomination. Stewart L. Woodford of New York withdrew his own name from consideration as it was not done at his suggestion.
Representative William A. Wheeler of New York was thirteen votes shy of a majority on a partial first ballot when the rules were suspended so that he could be nominated by acclamation. Wheeler defeated Frederick T. Frelinghuysen of New Jersey, Marshall Jewell and Joseph R. Hawley of Connecticut for the nomination.
| Vice Presidential Ballot[4] | |
|---|---|
| Ballot | 1st (Partial Roll-Call) |
| Wheeler | 366 |
| Frelinghuysen | 89 |
| Jewell | 86 |
| Woodford | 70 |
| Hawley | 25 |
| Not Called | 120 |
Vice Presidential Balloting / 3rd Day of Convention (June 16, 1876)
-
1st
Vice Presidential Ballot
(Partial)
See also[edit]
- History of the United States Republican Party
- List of Republican National Conventions
- U.S. presidential nomination convention
- 1876 United States presidential election
- 1876 Democratic National Convention
References[edit]
- ^ McFeely, William S. (1981). Grant: A Biography. Norton. pp. 440–441. ISBN 0-393-01372-3.
- ^ Patrick, Rembert W. (1968). The Reconstruction of the Nation. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 255. ISBN 0-195-01016-7.
- ^ Heymann, C. David (1980). American Aristocracy: The Lives and Times of James Russell, Amy, and Robert Lowell. New York: Dodd, Mead & Company. p. 136. ISBN 0-396-07608-4.
- ^ Republican party. National convention. 6th, Cincinnati; Clancy, A. M.; Nelson, William (10 April 1876). "Proceedings of the Republican national convention, held at Cincinnati, Ohio ... June 14, 15, and 16, 1876 ." Concord, N.H., Republic press association. Retrieved 10 April 2018 – via Internet Archive.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
External links[edit]
- Republican Party Platform of 1876 at The American Presidency Project
- Proceedings of the Republican National Convention, Held at Cincinnati, Ohio, Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday, June 14, 15, and 16, 1876
| Preceded by 1872 Philadelphia |
Republican National Conventions | Succeeded by 1880 Chicago |

.jpg/99px-President_Rutherford_Hayes_1870_-_1880_Restored_(cropped).jpg)



.jpg/85px-Roscoe_Conkling_c._1868_(cropped).jpg)

.jpg/90px-Marshall_Jewell_-_NARA_-_530329_(3x4a).jpg)





.jpg/95px-VicePresident-WmAlWheeler_(cropped).jpg)
.jpg/91px-Frederick_T._Frelinghuysen_-_Brady-Handy_(cropped).jpg)
.jpg/95px-Gen._Stewart_L._Woodford_c._1860s_(cropped).jpg)